Your lungs are struggling. Each breath feels like work. The room spins slightly as you try to sit up in bed.
This is what happens when pneumonia takes hold. And this is exactly when medical oxygen becomes not just helpful, but potentially lifesaving.
What Actually Happens When Pneumonia Attacks Your Lungs
Think of your lungs as a vast network of tiny air sacs called alveoli. In a healthy person, these sacs fill with air, allowing oxygen to pass into your bloodstream while carbon dioxide flows out. It’s an elegant exchange that happens millions of times a day without you even thinking about it.
But when pneumonia strikes, inflammatory exudate fills these alveoli, causing significant volume loss and reducing the lung’s ability to inflate properly. The infection triggers inflammation, and fluid begins accumulating exactly where air should be. Your lungs become heavy, congested, and unable to perform their primary job.
The result? Your blood oxygen levels drop below normal, a condition known as hypoxemia. Without enough oxygen circulating through your body, your organs start suffering. Your brain gets foggy. Your heart races, trying to compensate. Every cell in your body begins screaming for what it can’t get.
The Science Behind Why Oxygen Therapy Works
Medical oxygen therapy isn’t just about making breathing easier (though that’s certainly part of it). It’s about preventing a dangerous cascade of events that happens when your body doesn’t get enough oxygen.
Research shows that hypoxia itself can amplify inflammation in the lungs, creating a feedback loop where low oxygen levels trigger more inflammation, which further reduces oxygen levels. Breaking this cycle becomes critical.
When pneumonia fills your alveoli with fluid, blood continues flowing through these consolidated areas of the lung, but no gas exchange occurs, creating what doctors call an intrapulmonary shunt. It’s like having blood bypass a rest stop it desperately needs to make. Supplemental oxygen increases the concentration of oxygen in the remaining functional lung tissue, giving your body a fighting chance to maintain adequate oxygen levels in your bloodstream.
Oxygen therapy prevents organ failure by ensuring vital organs receive adequate oxygenation even when lung function is compromised. Your brain, heart, kidneys… they all need oxygen to function. When they don’t get it, damage happens quickly. Sometimes irreversibly.
When Doctors Prescribe Oxygen for Lung Infections
Not everyone with pneumonia needs supplemental oxygen. But when they do, timing matters.
Oxygen therapy is typically initiated when oxygen saturation drops below 92% in healthy adults, though the target range may differ for patients with chronic lung conditions. Doctors monitor your oxygen levels using a small device clipped to your finger called a pulse oximeter. When those numbers fall, action needs to be swift.
In severe cases of hypoxemia, oxygen should be administered immediately using a non-rebreathing reservoir mask at flow rates of at least 15 liters per minute. This isn’t subtle medicine. It’s an aggressive intervention because the stakes are high.
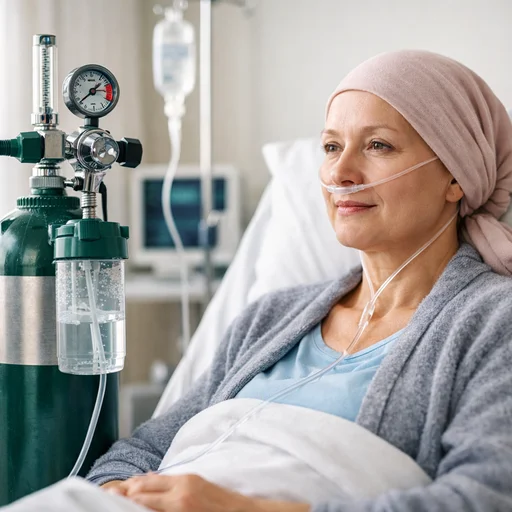
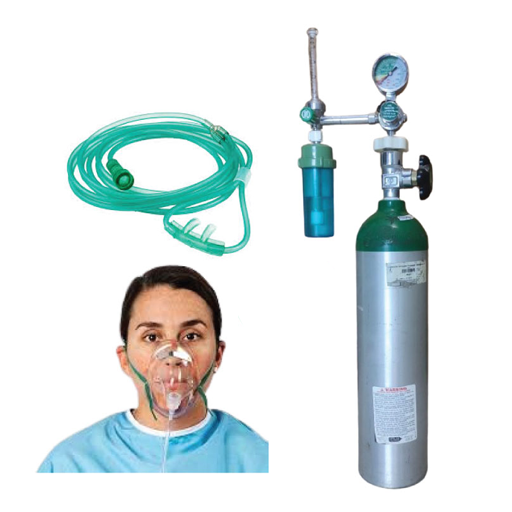
The delivery method depends on how much help your lungs need. A nasal cannula works for mild cases. Face masks for moderate needs. And for severe pneumonia? Non-invasive ventilation devices like CPAP and BiPAP machines provide both oxygen and pressure support to ease the work of breathing.
Different Types of Oxygen Delivery Systems
Walking into a hospital room where someone is receiving oxygen therapy can feel overwhelming. The equipment varies based on severity and need.
Nasal Cannula: Those thin plastic tubes that rest in the nostrils. They deliver 1 to 6 liters per minute of oxygen flow and work well for patients who need modest supplementation. They’re comfortable enough to wear while eating, talking, or sleeping.
Oxygen Masks: These cover both nose and mouth. Standard face masks deliver 6 to 10 liters per minute, providing higher oxygen concentrations than nasal cannulas. Some people find them claustrophobic, but they’re necessary when needs increase.
Venturi Masks: Precision matters here. These masks deliver exact oxygen percentages, which becomes important for patients with certain chronic conditions where too much oxygen can actually cause problems.
Non-Invasive Ventilation: When breathing itself becomes exhausting, machines like BiPAP don’t just deliver oxygen… they help push air into the lungs with each breath, reducing the work your respiratory muscles must do.
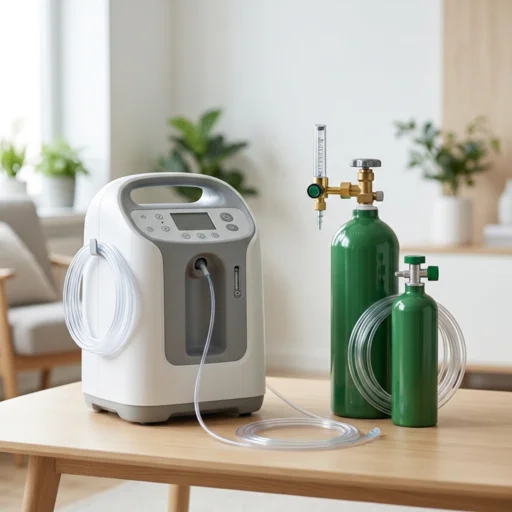
For patients in Bangladesh dealing with serious respiratory infections, having access to reliable medical equipment becomes a matter of survival. Companies like Marium Oxygen provide not just oxygen cylinders and oxygen concentrators, but also critical respiratory support devices including CPAP machines and pulse oximeters that help monitor oxygen levels at home.
The Benefits Go Beyond Just Breathing Better
Yes, oxygen therapy helps you breathe. But the benefits run deeper than that surface relief.
Studies show that oxygen therapy shortens hospital stays, allowing pneumonia patients to recover faster and return to normal activities sooner. Fewer days in a hospital bed means less exposure to other infections, less time away from family, and lower medical costs.
Non-invasive ventilation can reduce the risk of death in intensive care units, decrease the need for intubation, and shorten ICU stays. Intubation means having a tube placed down your throat and being connected to a ventilator. Avoiding that step represents a massive difference in patient experience and outcomes.
The psychological impact matters too. When you can’t breathe, panic sets in. Oxygen therapy provides immediate relief from that terrifying sensation of suffocation. It allows patients to rest, which the body desperately needs for healing.
Potential Risks and Careful Monitoring
Like any medical intervention, oxygen therapy isn’t without considerations. Too little oxygen is dangerous. But too much can cause problems as well.
High oxygen concentrations can damage lung tissue and lead to complications like carbon dioxide retention or acute respiratory distress syndrome. This is why healthcare providers monitor oxygen levels closely and adjust delivery rates based on continuous assessment.
Research has shown that high concentration oxygen therapy can increase carbon dioxide levels in pneumonia patients, which is why modern protocols focus on titrating oxygen to maintain adequate but not excessive levels.
Healthcare professionals trained to recognize signs of oxygen toxicity regularly monitor respiratory rate, oxygen saturation levels, and other vital signs. It’s a balance… providing enough to prevent organ damage while avoiding the complications of over-oxygenation.
Oxygen Therapy as Part of Complete Pneumonia Treatment
Here’s what people sometimes miss: oxygen alone doesn’t cure pneumonia. It’s one critical piece of a larger treatment plan.
Bacterial pneumonia requires antibiotics, and it’s important to complete the entire course even after symptoms improve. The oxygen helps you stay stable while the antibiotics fight the infection. Viral pneumonia might require antiviral medications. Fungal infections need antifungal drugs.
Treatment also includes adequate rest, staying hydrated, and managing symptoms like fever and body aches. Your body is fighting a war. It needs resources: medication, oxygen, fluids, rest, and time.
For those recovering at home with milder cases, having access to home oxygen equipment can make the difference between a hospital admission and safe recovery at home. Many patients in Dhaka benefit from home oxygen services that provide not just equipment, but guidance on proper use and 24/7 support for emergencies.
Recovery Takes Time
Even after the infection clears and oxygen therapy ends, your lungs need time to fully heal. Some people recover within a week, but for others, full recovery takes a month or longer. Rushing back to normal activities too soon risks relapse.
Your healthcare provider will monitor your progress and let you know when it’s safe to discontinue oxygen therapy. The goal is maintaining stable oxygen levels without supplementation. Until then, patience becomes as important as any medication.
The reality is
Medical oxygen therapy for pneumonia and serious lung infections isn’t optional care. It’s a fundamental intervention that maintains life while your body fights infection.
When pneumonia fills your lungs with fluid and inflammation, supplemental oxygen ensures your organs continue receiving what they need to function. It prevents the dangerous cascade of events that occurs when oxygen levels plummet. It reduces the work of breathing, allowing your body to direct energy toward healing. And in severe cases, it quite literally means the difference between survival and organ failure.
If you or someone you love develops pneumonia, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. Early intervention, including oxygen therapy when indicated, dramatically improves outcomes. Pay attention to warning signs like rapid breathing, confusion, bluish lips or fingernails, and oxygen saturation levels below 90%. These indicate the need for immediate medical evaluation.
Your lungs do remarkable work every moment of every day. When they need help, modern medicine offers powerful support. Oxygen therapy represents one of the most important tools in that arsenal… simple in concept, profound in impact.